Table of Contents
Review the comprehensive profile of commonplace Firefox malware and leverage the cleanup steps to remove potentially unwanted programs from this browser.
According to the latest stats on global web browser share, Mozilla Firefox makes it to the top three, with about half a billion customers using it across the planet, and that’s notwithstanding the extremely strong competition in the niche. It is an open-source browser compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, Mac OS X and Android.
Firefox is not flawless. It is subject to occasional crashes and other performance-related issues. That’s not something out of the ordinary, though, because no web browser is perfect. To their credit, the Mozilla tech teams are rolling out security and stability updates on a regular basis, patching known vulnerabilities, addressing potential exploitation scenarios and preventing lags. All in all, the vendor is undoubtedly doing their best to stay on top of the contemporary trends and challenges. In spite of that, users keep getting infected with adware and hijackers that make quite a fly in the ointment. Why is that happening? Most of the time, the weak link isn’t the browser itself. It’s the human error. The prevalent compromise workflow is as follows: people download and install various applications and overlook some inconspicuous options that are already activated by default.
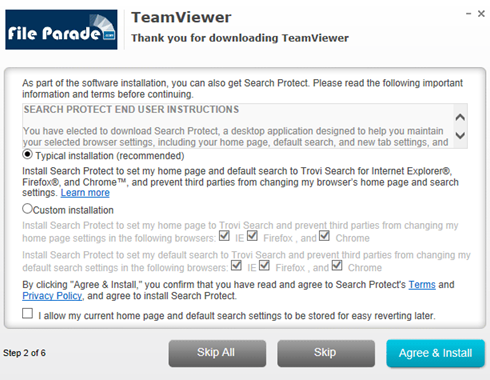
Take a look at the screenshot above. It reflects a very typical browser infection process, although everything looks fairly legal and normal at first sight. In a nutshell, evading contamination by the homepage and search hijacker called Trovi Search in this case is a matter of unticking one or a few checkmarks or radio buttons – as simple as that. This happens when the user is installing an absolutely different applet, whose recommended installation package already contains the malware. Not too many people actually peruse these screens, and the bad guys know it. Being meticulous and reading the setup terms, especially when installing freeware programs, is a great habit that helps stay clear of a lot of malicious stuff on the Internet.
Malware samples tailored for Firefox are innumerable in their quantity but they aren’t very versatile as far as the operational patterns are concerned. Basically, the most widespread types of these bugs are ones that incorporate sponsored objects into visited sites and the ones that distort custom browsing settings to reorganize the web traffic on the targeted machine. In either case, the ultimate idea is to display ads which, as we all know, get paid for. Hijacked web traffic can also be converted into tangible profit. It’s also noteworthy that these infections tend to be disguised as Firefox add-ons, web service enhancement tools or plugins.
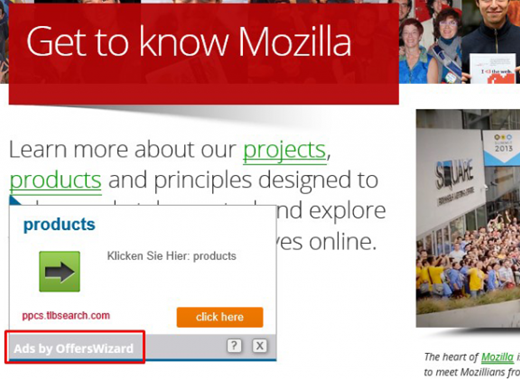
The advertisements generated by Firefox viruses include links above the fold built into SERPs (search engine results pages), comparison shopping sections, intrusive software download recommendations, discounts, freebies, interstitial ads and in-text links. The latter objects are particularly annoying as they inflate the entire web page space and users can accidentally click on them when scrolling up and down. At the end of the day, malware turns the victim’s browser into a clear-cut malvertising platform without asking for permission.
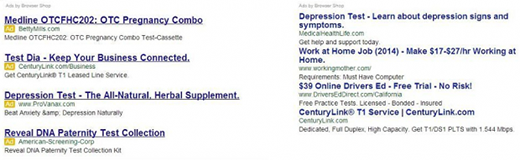
Unfortunately, no matter how safe the web browser is, malicious software is going to get in if the user isn’t prudent enough. Again, it’s critical to review setup options when installing free software via Firefox. Also, skipping the patches recommended by Mozilla might get you in trouble, so be sure to adopt them once they become available. A reliable security tool can block potentially unwanted code in real time, so it’s a must-have. But if you happen to have already gotten your Firefox compromised, follow the instructions below to erase the threat for good.
Techniques to remove malware from Firefox
There are several vectors applicable to eradicate malicious code that ended up in your browser. Since both search hijackers and ad-inserting bugs tend to be embodied as malicious extensions or plugins, the first workaround is to uninstall these apps. While this approach is often efficient, sometimes it won’t work – it all depends on severity of a particular threat. In the worst case scenario, refreshing Firefox works flawlessly, but this procedure will erase all personalized browsing data. So try the former technique first, and if it doesn’t help, proceed to the latter (steps to be provided below).
Method 1: Manual removal of malicious components from Firefox
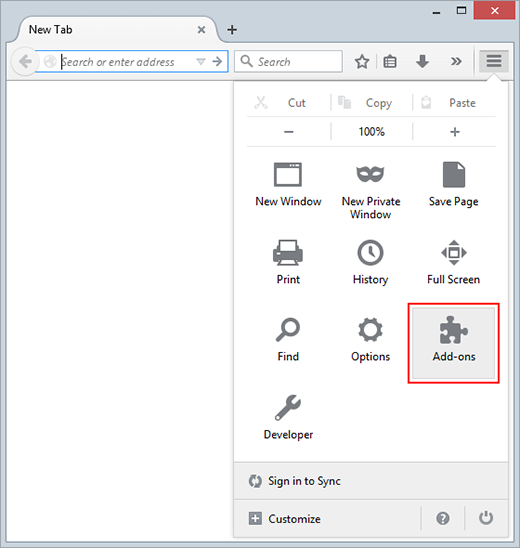
- Go to Firefox menu and select Add-ons

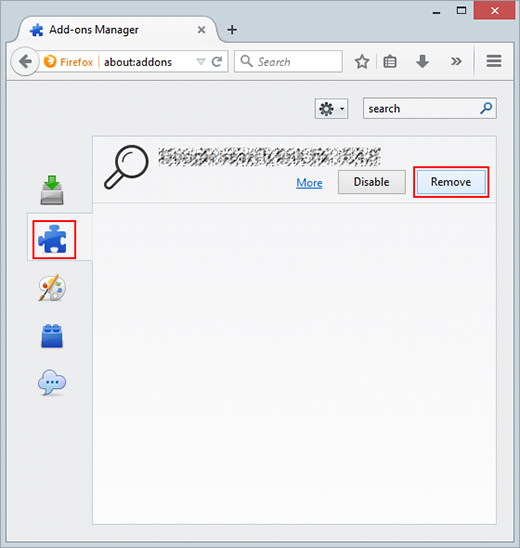
- Select Extensions on the screen, and uninstall the malicious object by clicking the Remove button

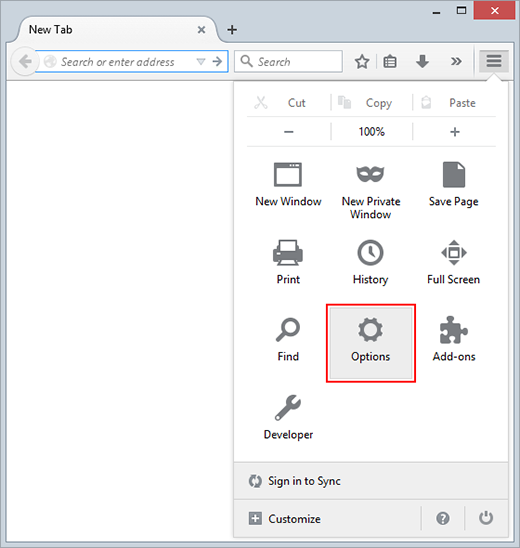
- Go back to Firefox menu and select Options

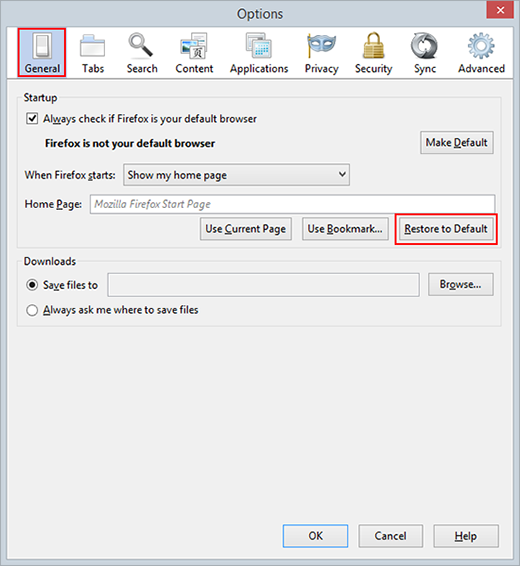
- Pick the General tab at the top and click Restore to Default in the Home Page section

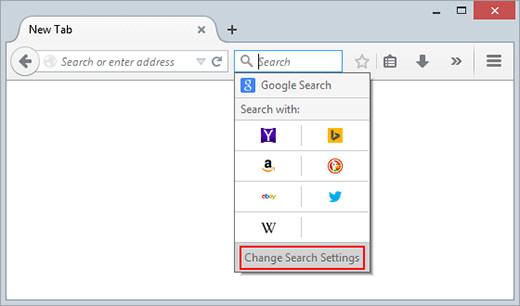
- Proceed to the Search tab on the same interface or click the magnifying glass icon in the search toolbar and select Change Search Settings option

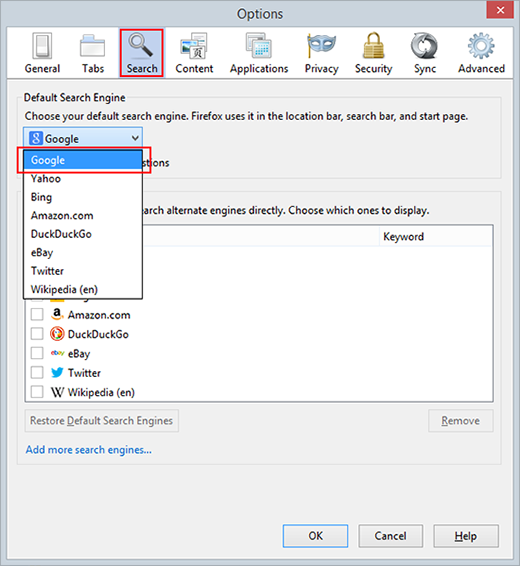
- In the Default Search Engine subsection, select your preferred provider and save the changes

- Restart Firefox and browse around a bit to check if the problem has been fixed. If the symptoms aren’t occurring anymore, you’re good to go. In the event the issue persists, move on to the next troubleshooting vector.
Method 2: Refresh Firefox to its original state
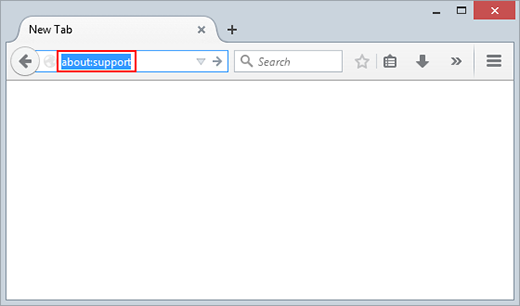
- Type about:support in the URL field and press Enter

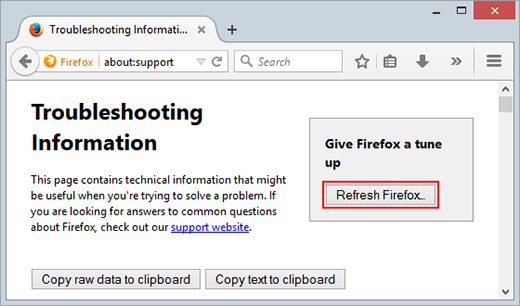
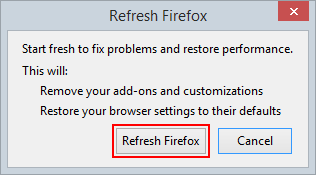
- Firefox will display the Troubleshooting Information page. Click Refresh Firefox as shown on the image below

- In the popup dialog that appeared, click Refresh Firefox to confirm

- Do some test browsing to see if things are okay now and whether the malware is gone.
Verify whether the virus has been completely removed from Firefox
Computer threats like the Firefox malware virus can be stealthier than you can imagine, skillfully obfuscating their components inside a compromised computer to evade removal. Therefore, by running an additional security scan you will dot the i’s and cross the t’s in terms of the cleanup.